Acute Upper Respiratory Infection
Acute Upper
Respiratory Infection (URI)
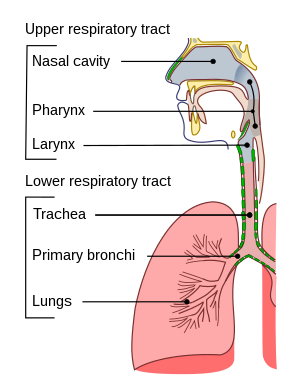
An acute URI is a contagious infection of your upper
respiratory tract. Your upper respiratory tract includes the nose, throat,
pharynx, larynx, and bronchi.
Without a doubt, the common cold is the most well-known
URI. Other types of URIs include sinusitis, pharyngitis, epiglottitis, and
tracheobronchitis. Influenza, on the other hand, isn’t an URI because it’s a
systemic illness.
Types of acute upper respiratory infection:
1. Common
Cold
2. Sinusitis
- inflammation of the sinuses.
3. Epiglottitis
- inflammation of the epiglottis, the upper part of your trachea. It protects
the airway from foreign particles that could get into the lungs. Swelling of
the epiglottis is dangerous because it can block the flow of air into the
trachea.
4. Laryngitis
- inflammation of the larynx or voice box.
5. Bronchitis
- inflammation of the bronchial tubes. The right and left bronchial tubes
branch off from the trachea and go to the right and left lungs.
Symptoms of acute upper respiratory infection:
A runny nose, nasal congestion, sneezing, cough, and
sputum production are the hallmark symptoms of URIs. Symptoms are caused by
inflammation of the mucous membranes in the upper respiratory tract. Other
symptoms include:
fever
fatigue
headache
pain during swallowing
wheezing (Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound made
while you breathe. It’s heard most clearly when you exhale, but in severe
cases, it can be heard when you inhale. It’s caused by narrowed airways or
inflammation. Wheezing may be a symptom of a serious breathing problem that
requires diagnosis and treatment.)
How is acute upper respiratory infection diagnosed?
Most people with URIs know what they have. They may visit
their doctor for relief from symptoms. Most URIs are diagnosed by looking at a
person’s medical history and doing a physical exam. Tests that may be used to
diagnose URIs are:
Throat swab. Rapid antigen detection can be used to
diagnose group A beta-hemolytic strep quickly.
Lateral neck X-rays. This test may be ordered to rule out
epiglottitis if you have difficulty breathing.
Chest X-ray. Your doctor may order this test if they
suspect pneumonia.
CT scan. This may be used to diagnose sinusitis.
How is acute upper respiratory infection treated?
URIs are mostly treated for relief of symptoms. Some
people benefit from the use of cough suppressants, expectorants, vitamin C, and
zinc to reduce symptoms or shorten the duration.
Other treatments include the following:
Nasal decongestants can improve breathing. But the
treatment may be less effective with repeated use and can cause rebound nasal
congestion.
Steam inhalation and gargling with salt water are a safe
way to get relief from URI symptoms.
Analgesics like acetaminophen and NSAIDs can help reduce
fever, aches, and pains.

Comments
Post a Comment